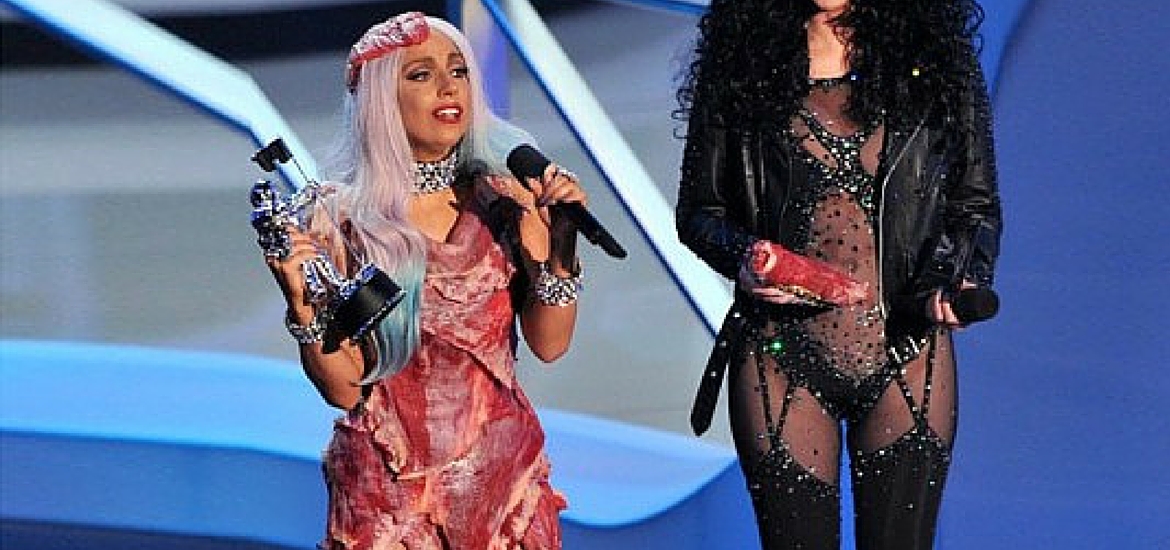
Questions of Gender Identity
Our society struggles with how to understand gender identity.
Some people have concrete ideas of what it means to be a man or a woman while others question if there are any traits essential to gender. Each group seems to be attempting to bend society to their preferences, whether for stricter gender conformity or for a move towards androgyny or multiplicity.
In Christian theology, questions of gender are taking place not only horizontally in society, but also vertically: is God masculine or feminine? Is it acceptable to use both feminine and masculine pronouns when referring to God? Might it even be preferable to do so?
In the first novel of her Hunger Games trilogy, Suzanne Collins presents an image of a post-gender society that helps us imagine the Kingdom of God as a reality. In this dystopian society, individuals live out of true identity without pressure to conform to a predetermined concept of gender identity.
Gender Identity in Katniss & Peeta
The main characters of The Hunger Games, Katniss and Peeta, give a glimpse of gender within the Kingdom of God. They do not conform the gender norms that exist in of our current society, and thus question the existence of such societal norms.
Peeta, an artistically gifted baker, values connection over hierarchy and bonds through shared feelings at least as much as shared experiences — qualities considered feminine by contemporary USAmerican society. Because of his traditionally feminine qualities, many are interested in Peeta’s portrayal of feminized masculinity; some reviewers have even criticized Collins for having unfavorably over-feminized a lead character.
Katniss is a hunter. She is stoic and emotionally distant, at times out-of-touch with her own emotions and those of others.
It is easy to view the relationship between Katniss and Peeta as a gender-role reversal. In their vocations, they go against the norms. In their emotional awareness and capacity, they defy our expectations. However, such statements assume that the culturally constructed norms of gender we hold today are in some way intrinsic to males and females.
Reviewers attempting to place our current understanding of gender onto Peeta and Katniss have a hard time of it. Writing for Bitch Media, Kelsey Wallace concludes her character evaluation of Peeta: “If Gale is the bad boy, Peeta is, well, something else. Not the good boy exactly, but maybe the nice boy.” In some way, Peeta resists categorization.
Gender Identity in Panem
Indeed, the entire society of Panem seems to resist categorization to the extent that it could be described as post-gender. In District Twelve, survival matters more than conformity so much so that no one seems surprised by a girl who ventures outside the protection of the fence to hunt and gather. The other spectrum of society, in the Capitol, also defies our current gender norms, as both men and women seem to be equally concerned with fashion and makeup.
Rather than imposing our society onto Panem and its inhabitants, we would be wise to allow the text to question our internalized understanding of gender roles. Why are we, the readers, surprised by a female archer, or a man in makeup? Why are some of us angered by Peeta’s vulnerability, or by Katniss’s inability to intuit Peeta’s emotions? We have been so indoctrinated by the gender norms of our culture that we can’t even see past them when another society, another way of being, is presented.
Identity Beyond Gender
Collins offers her readers a new way of looking at gender. While Katniss is preparing for the pre-Games interview, she is trying to figure out how best to present herself: “charming? Aloof? Fierce? … I’m too ‘vulnerable’ for ferocity. I’m not witty. Funny. Sexy. Or mysterious.” Unable to categorize herself in either (from today’s standpoint) feminine or masculine roles, she vents to her stylist: “I just can’t be one of those people [my coach] wants me to be.” Like many individuals in today’s world, Katniss just can’t force herself to fit into a culturally-dictated cookie-cutter role, regardless of its femininity or masculinity.
Cinna offers a solution to both Katniss and the reader that is at once obvious and beautiful:
“Why don’t you just be yourself?”
Amidst the questions of Katniss’s combination of masculine and feminine traits and Peeta’s feminized depiction, critics have missed Cinna’s prophecy. Is Katniss a masculine woman? Is Peeta a feminine man? Within the world of the novel, the questions don’t apply: Katniss is Katniss; Peeta is Peeta. The characters are fully themselves, in the full complexity of their gender.
The Identity of God
Personification
The God of the Bible includes both feminine and masculine traits. In the beginning, God creates “male and female” in the image of God’s self. Scripture describes God with masculine images such as father (e.g., Hosea 11:1) and king (e.g., Psalm 29:10), as well as feminine depictions such as mother (e.g., Isaiah 66:13).
Surely, this is a God whose identity is reflected by both men and women. God’s gender is carried by the diversity of masculine and feminine individuals; it feels safe to imagine that the Kingdom of God will not only tolerate masculine and feminine genders but will accept and celebrate such diversity.
And yet, such a view, as hopeful as it sounds, is too limited, too unimaginative. The God of scripture includes and transcends gender. From the anthropomorphic images of God as father, king, and mother, we could easily picture God as a male or female figure. However, to do so would be to misconstrue the characteristic being invoked.
As Hebrew scholar David Stein notes, “Personification was employed as a vehicle to convey a statement about deity—and especially about one’s relationship with deity.” What is being invoked in the image of father or mother is an aspect of relationship, a situational similarity, rather than the full, embodied, engendered being.
Such an understanding of the text gives a clearer understanding of what the scriptural author wants to invoke in the audience. It also clarifies seemingly paradoxical images, such as “suck at the breast of kings”, in which a female biological function of nursing is ascribed to male rulers. To understand the personifications of God too literally means to deny the grand all-ness of a Divinity that transcends all human boundaries and definition, including gender.
Beyond Every Human Category
Genesis 1 not only sets the stage for the entire story, it introduces the character and event of God with a powerful first impression of a being who is beyond every human category. This God creates and orders the universe with a word; it is part of this deity’s identity to surpass all traits of humans, meaning that this being is almost nothing like a human. Such a God is so other that “the audience not only receives no warrant to ascribe social gender, but would be hard pressed to do so,” writes Stein.
Just as Collins’s created society of Panem does not ask questions of Katniss’s nor Peeta’s gender, the audience of scripture receives no warrant to ascribe social gender to God. Those who do have an equally hard time, as demonstrated above. Stein, emphasizing the importance of first impressions, summarizes the rule for understanding the transcendent inclusiveness of God with regards to gender: “What is inappropriate to the opening, do not do what’s joined to it—that is, the whole Torah.”
How, then, should gender be understood in a Kingdom that lives under a God who is introduced to be beyond human understanding?
Why Don’t You Just Be Yourself?
Christian theologians have been easily sidetracked by our own understandings of gender and identity in the debate over God’s masculine and feminine descriptions. Some attempt to equally disperse masculine and feminine pronouns, others try to discern which parts of the Trinity are which gender. As a solution, to paraphrase Cinna, why don’t we just let God be God?
If Christians are to read Scripture to understand the character of God, as the people of ancient Israel did, we must not allow vision to be clouded by the predominant culture’s misunderstandings and false truths. Doing so would be to superimpose our paradigm onto God, effectively killing the living God and creating an idol in humanity’s image. Just as readers of The Hunger Games can fully appreciate the narrative by allowing Katniss and Peeta to live out of their truest selves, so should even the most critical reader of scripture allow God to be the true God, without attempts to superimpose a gendered box onto Her/Him God.
A Kingdom Understanding of Gender
A Kingdom understanding of gender must reflect a God who acts uniquely and creates humanity in God’s image.
Although a dystopia, Panem presents a society that appears to be largely beyond concerns of gender roles, whether such nonchalance is the result of desperate survival, as it is in District Twelve, or boredom and body decoration, as it is in the Capitol. In Panem, people are intrigued and impressed by the full identity of Katniss, not only that she is at once strong and female. Even more so, the audience of the Games is captivated by Peeta’s emotional vulnerability and intuitive ability to connect, and not only because he is a man doing so. Rather than praising individuals for breaking gender boundaries, Panem is a society that allows individuals to live out of their truest identity and understanding of self.
May we anticipate a Kingdom in which we are accepted and celebrated for living out of our true self rather than a societal expectation, in which the complexity of an individual’s gender-sex alignment is secondary to the fullness and flourishing of individual identity.

Questions: Did you have any reactions to the gender of Peeta or Katniss while reading/viewing The Hunger Games? What did that reaction tell you about yourself and how you understand gender? What would you do with your life if it didn’t make you a “bad woman/man”?

 Our church foremothers and forefathers did not develop an understanding of sin so that we could do more sin. The vocabulary of sin is meant to give us sight for the ways we are blocked from participation in love. Understanding the ways we don’t receive God’s gifts can help us find ways to outstretch our arms for those gifts. Understanding sin enables broken people to be made whole in God’s love.
Our church foremothers and forefathers did not develop an understanding of sin so that we could do more sin. The vocabulary of sin is meant to give us sight for the ways we are blocked from participation in love. Understanding the ways we don’t receive God’s gifts can help us find ways to outstretch our arms for those gifts. Understanding sin enables broken people to be made whole in God’s love.


 Whenever salvation or grace is preached, what is implicit is the notion of salvation from a state of being, or grace with regards to a tendency. The word ‘sin’ may not be used, but its presence is assumed when we use the words like salvation, redemption, and grace.
Whenever salvation or grace is preached, what is implicit is the notion of salvation from a state of being, or grace with regards to a tendency. The word ‘sin’ may not be used, but its presence is assumed when we use the words like salvation, redemption, and grace. It is not enough to be converted to a new way of life once. We must be converted freshly every day – at times it feels we must be converted every hour – and continuously re-oriented toward the goal. The goal, by the way, is love of God and neighbor.
It is not enough to be converted to a new way of life once. We must be converted freshly every day – at times it feels we must be converted every hour – and continuously re-oriented toward the goal. The goal, by the way, is love of God and neighbor.







![The Prophetic Works of Lady Gaga - [from Literate Theology]](https://kateraedavis.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/01/prophet-gaga-1.jpg)





